
Sitting on hard surfaces causes sit bone pain These are also some of the reasons for sacroiliac joint pain. Risk factors that can cause stress fractures in your sit bone are running long distances, trauma that bruises the bones in your buttocks, or intense exercising. Other reasons for stress fractures on the ischial tuberosity are overuse injuries and too much pressure on the pelvic bone. Damage to the sit bone can occur when the hip is suddenly flexed. Researchers found that ischial tuberosity injuries have similar symptoms to hamstring injuries. Ischial tuberosity stress fracture from exercisingĪ stress fracture in your ischial tuberosity from exercising or from wear and tear is a common reason for buttock pain as well as pelvic bone pain when sitting.Īccording to the journal Hip & Pelvis, pain in the pelvic area can occur due to small stress fractures in the pelvic bones. Let’s look at some of the most common causes of butt bone pain when sitting that comes from your ischial tuberosity. If your hamstring is affected then you could have weakness in one or both of your legs and it may affect your gait. The Journal of the Hip Preservation Society says that pain in the sit bone can also be a reason for groin pain and pain in the center of your buttocks.
This can cause inner thigh pain and also tingling or numbness in your leg. A trapped sciatic nerve can cause lower back pain (lumbar pain) with pain and/or tingling sensations that radiate down your leg.
4Īnother symptom of sit bone pain occurs if your sciatic nerve is involved. This can also affect muscles and ligaments in your lower legs. The Journal of Korean Neurosurgical Society reports that prolonged sitting on hard surfaces will result in pain and numbness in your buttocks. However, depending on the extent of damage to your ischial tuberosity and other ligaments, muscles, or nerves involved, you will have associated symptoms. Pain when sitting down is one of the main symptoms of sit bone pain. 2Īccording to the Merriam Webster dictionary, the main function of your sit bone is to bear your body weight when sitting.
Also, your hamstring is connected to your sit bone as well as your sciatic nerve. For example, ligaments attach to your gluteus maximus which are necessary to keep your upper body stable. The University of Michigan Medical School reports that various ligaments and muscles attach to your ischium bones.

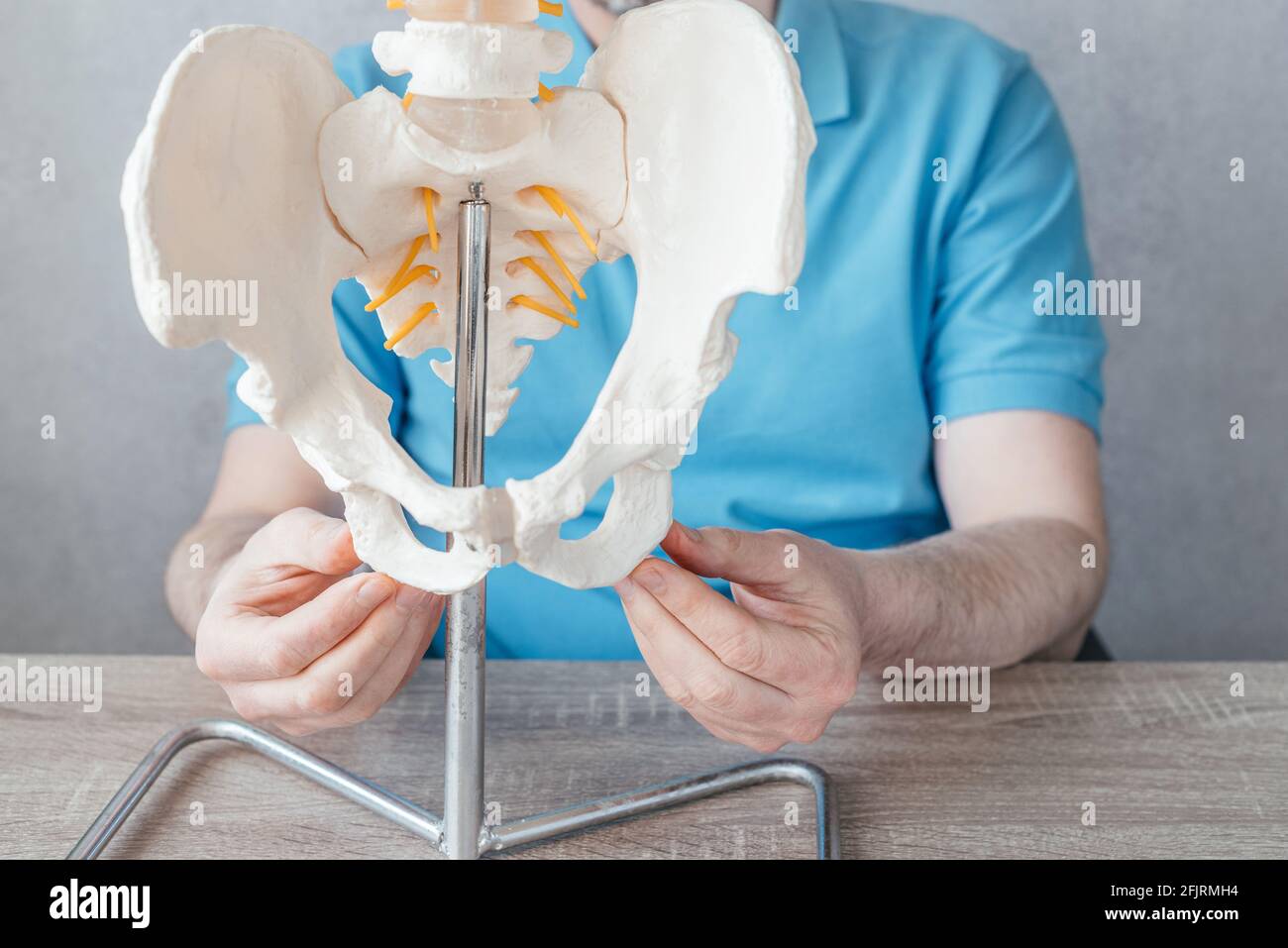
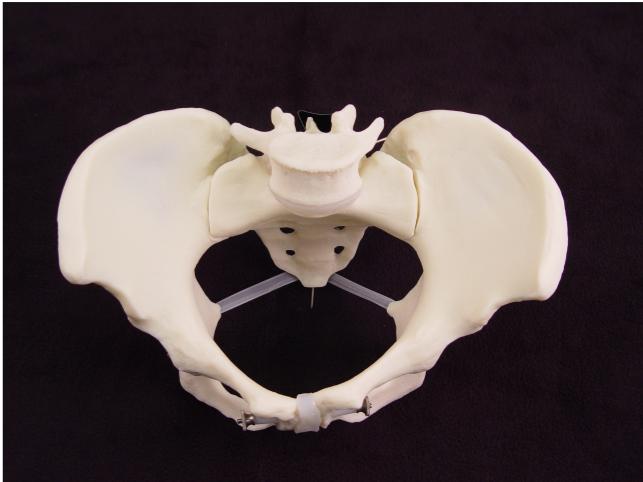
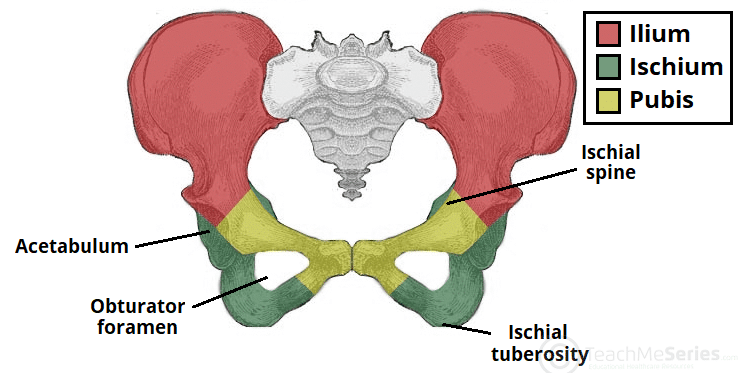
Both have a slightly triangular shape and these are the bones that you sit on. The thick lower part of the bone is called the ischial tuberosity and you have one on either side of your buttocks. The sit bone is a bony protrusion at the base of your pelvic bones.Īccording to the University of the West of England, the ischium is divided into an upper part and lower part. The dissection planes and the different pelvic spaces used for surgery are explained, insisting on the main vessels, nerves, plexus, ureters which are obstacles to bear in mind and to avoid.The sit bone (ischial tuberosity) is sometimes referred to as the sitz bone, sits bone, or sitting bone. Approximately 90 laparoscopic anatomy pictures are presented in this authoritative lecture. The four attachment sites which may be used by the surgeon for fascia and pelvic organ attachment in POP surgery are discussed- Cooper’s ligament, white line, ischial spine, and sacral promontory. Visceral ligaments occupy an anteroposterior axis (pubovesical ligaments, bladder pillars, and uterosacral ligaments) and a transverse axis (lateral bladder ligaments, cardinal ligaments, paracervix and rectal pillars). Traditional anatomy considers three levels: pelvic and perineal muscles, ligaments, and the space between all fascias covering the organs. In this key lecture, Professor Jean-Bernard Dubuisson delineates the laparoscopic pelvic floor anatomy involved in surgical procedures for the management of pelvic organ prolapse (POP) and urinary incontinence.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
